Explain the Major Differences Between Pathogenic and Nonpathogenic Bacteria
7 rows The main difference between pathogenic and nonpathogenic bacteria is that the pathogenic. Using the well-differentiated colonic carcinoma cell line T-84 as a model epithelial layer Madara et al.

Major Bacteria Present Probiotics Microorganisms In Healthy Humans Probiotics What Are Probiotics Human Microbiome Project
Fungi are more complicated organisms than viruses and bacteriathey are eukaryotes which means they have cells.
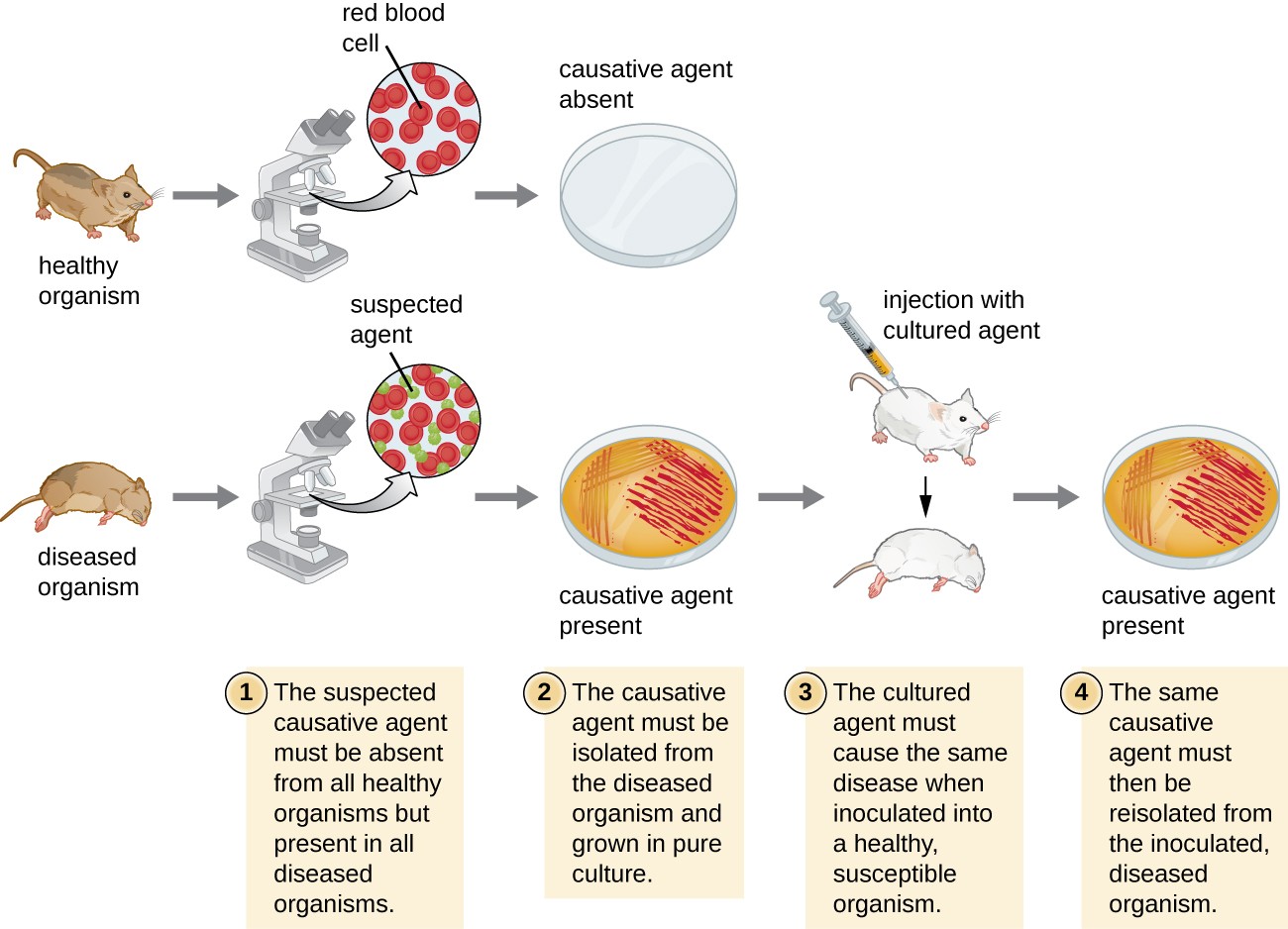
. In 1890 the German physician Robert Koch formalized the criteria to classify bacteria as pathogenic. What is the difference between pathogenic bacteria and pathogenic virus. Bacteria can be beneficial as well as harmful.
Pathogens such as Staphlococcus Vibrio cholera and Mycobacterium tuberculosis differ from normal non-pathogenic microbes in that they cause damage to the host. These pathogenic species are usually distinct from the usually harmless bacteria of the normal gut flora. Reported dramatic differences between pathogenic and nonpathogenic bacteria in activating this critical signaling pathway Science 20002891560-1563.
Pathogenic bacteria have certain genes and characteristics that endow them with the capacity to cause disease. Non-Pathogenic microorganisms are incapable of causing disease. Of the three pathogens fungi are most similar to animals in their structure.
Some nonpathogenic bacteria inhibit the pathway by blocking the ubiquitination Ub of IκB. Coli strains to train a PCA-SVM model. What is the difference between pathogenic bacteria and non pathogenic bacteria.
The distinction between the two can be made based on the Kochs Postulates. Around 99 of bacteria are nonpathogenic. How fungi makes us sick.
Beneficial bacteria can be found in dairy products like milk and yogurt. Systemic diseases caused by viral infection include influenza measles polio AIDS and COVID-19. Microorganisms were reported mainly in poultry meat meat.
But a different strain of the same species may be pathogenic. Using the well-differentiated colonic carcinoma cell line T-84 as a model epithelial layer Madara et al. Some strains of this group are used in the food industry and can be graded as non-pathogenic.
In reality the distinction is not always clear. So PCR test for on of the virulence genes or pathogenicity using experimental animals are two main cases enable us to know wheather the organism is pathogenic or. In this study we evaluated whether Raman microspectroscopy could be used to determine the pathogenicity of E.
The most frequently notified pathogenic microorganisms in the RASFF in 19802017 were Salmonella sp Listeria Escherichia and Vibrio whereas among the notified non-pathogenic microorganisms were unspecified microorganisms Enterobacteriaceae Salmonella sp. Pathogenic virus effects the immune system thus making the stomach and brain naseous. Pathogenic bacteria cause illness.
When it comes to food these include bacteria viruses and parasites. Bacterial gastroenteritis is caused by enteric pathogenic bacteria. Non-pathogenic bacteria peacefully co-exist with us and do not cause illness.
Pathogens can resist the hosts defence mechanisms. Ad Over 27000 video lessons and other resources youre guaranteed to find what you need. This review aims to work out the differences between the pathogenic properties of highly and medium-pathogenic staphylococcal species and to draw a comparison between the pathogenic species and the food-grade S.
By definition a pathogen is a specific cause of a disease while a non-pathogen is considered harmless. Pathogenic bacteria can be grouped into three categories on the basis of their invasive properties for eukaryotic cells Fig. Bacteria are more complex organisms than viruses and dont need a living host to thrive or reproduce.
They can live as mesophile. The first thing to do is learn the difference between food spoilage organisms and food pathogens that cause food-borne illness. Nonpathogenic bacteria lack these characteristics.
There are two main types of fungi. Some of them are autotrophs. Reported dramatic differences between pathogenic and nonpathogenic bacteria in activating this critical signaling pathway Science 20002891560-1563Previous investigators have shown that certain pathogenic bacteria such as wild-type Salmonella.
Viruses are only active within host cells which they need to reproduce while bacteria are single-celled organisms that produce their own energy and can reproduce on their own. Then the obtained model was tested by identifying the pathogenicity of three additional E. Although some bacteria eg Rickettsia Coxiella and Chlamydia grow only inside host cells others eg Salmonella Shigella and Yersinia are facultative intracellular pathogens invading cells when it gives them a selective advantage in.
Ie harmless to other organisms They mostly live in the environment as saprophytes. Environmental which are yeast and mold that often live in soil and dont generally cause. Examples that are commonly known are E.
The distinction is sometimes difficult as. One important characteristic is the capacity to adhere to tissues. This damage allows the pathogen to colonize novel sites antagonizes the host immune response and facilitates spread of the pathogen.
While pathogenic bacteria if. Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms that live almost everywhere. We used Raman spectra of seven non-pathogenic and seven pathogenic E.
Non pathogenic bacteria have affinity for various types of temperatures and they can sustain themselves in a particular type of environment only. Bacteria serve many vital roles in nature outside of being infectious. 13 rows Difference between pathogenic and non-pathogenic bacteria.
Coli noro virus and giardia but there are about 200 known food-borne pathogens in the world. A pathogen must do this in order to avoid removal from the body by the flow of fluids tears urine mucus. The terms pathogenic and non-pathogenic are often are applied to various microbes.
Main difference between these two is their adaptation according to environment.

How Pathogens Cause Disease Microbiology

Pathogenic Bacteria What Distinguishes A Pathogen From A Non Pathogen Ibiology

Pathogenic Bacteria What Distinguishes A Pathogen From A Non Pathogen Ibiology
No comments for "Explain the Major Differences Between Pathogenic and Nonpathogenic Bacteria"
Post a Comment